Beyond Bytes and Bits: Law Craft in the Information Age
The digital revolution has touched every aspect of modern life, and the realm of law is no exception. As technology continues to evolve, legal systems worldwide are grappling with the challenges and opportunities posed by the beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age. This article delves into how legal practices, frameworks, and principles are being reshaped by the digital era and explores the future of law in a rapidly changing landscape.
The Evolution of Legal Systems
Legal systems have always reflected the cultural, technological, and economic conditions of their time. Early laws were deeply rooted in tradition and religion, evolving over centuries to codify rights and responsibilities in societies.
In the digital age, however, the pace of change is unprecedented. The shift from physical interactions to virtual transactions has created legal grey areas that traditional frameworks were not designed to address. Issues such as online harassment, digital contracts, and cybercrimes have pushed lawmakers to rethink the foundations of their legal systems.
Technology and Its Influence on Legal Practices

Technology has profoundly influenced legal practices, transforming how lawyers, judges, and clients interact with the law. Tools like electronic filing systems and AI-powered legal research have streamlined processes that once took weeks or months.
Artificial intelligence, in particular, has become a game-changer in areas like contract analysis, case prediction, and even dispute resolution. By automating repetitive tasks, technology has enabled legal professionals to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of their work. However, the integration of AI also raises ethical and regulatory questions, particularly concerning transparency and bias.
Data Protection and Cybersecurity Laws
As data has become one of the most valuable resources of the modern era, the need for robust data protection and cybersecurity laws has grown. High-profile data breaches and the misuse of personal information have prompted governments worldwide to introduce stringent regulations to safeguard individuals and organizations.
Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States set benchmarks for data privacy. However, enforcing these laws across borders remains a significant challenge, given the global nature of digital activities.
Intellectual Property in the Digital Age
The rise of digital content has redefined the concept of intellectual property (IP). Creators now operate in a world where their work can be duplicated and distributed within seconds. While IP laws have evolved to protect digital assets, they often lag behind the pace of technological advancement.
Moreover, the tension between copyright enforcement and the demand for open access has sparked debates about how best to balance the interests of creators and consumers in the digital age.
The Legal Implications of Big Data
Big data has transformed industries by offering unprecedented insights into human behavior. However, its legal implications are vast and complex. From issues of consent and data ownership to the ethical use of analytics, the challenges of big data require careful legal scrutiny.
Legislators face the dual challenge of fostering innovation while protecting individual rights. Striking this balance will be crucial as big data continues to shape decision-making across industries.
The Future of Law in the Information Age

The future of law lies in its ability to adapt to a world where change is constant. Legal education is evolving to prepare future lawyers for challenges such as virtual courtrooms, blockchain-based contracts, and AI-driven legal systems. International cooperation will also play a critical role as nations work together to address cross-border legal issues.
Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that legal systems uphold justice and fairness while embracing the opportunities presented by technology. By doing so, the law can remain a cornerstone of society, even in a digital-first world.
This journey into the beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age underscores the importance of proactive, innovative approaches to law. As technology continues to transform society, the field of law must rise to the occasion, ensuring that justice is not only preserved but also enhanced in a world defined by bytes and bits.
Privacy vs. Public Interest
One of the most contentious legal debates of the beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age revolves around the conflict between privacy rights and the public interest. On one hand, individuals have a right to safeguard their personal data and maintain control over how it is used. On the other, governments and organizations argue that access to certain information is necessary for public safety, national security, and economic growth.
The Balance of Privacy Rights
Modern privacy laws aim to give individuals control over their digital footprint. These include the ability to opt out of data collection, request the deletion of personal data, and understand how their information is being used. Despite these advances, the boundaries of privacy remain blurred in situations where public interest outweighs individual rights.
For example, in cases of national security, surveillance technologies like facial recognition or metadata tracking are often employed. While these tools are instrumental in preventing crimes and identifying threats, they also raise concerns about misuse, overreach, and the erosion of personal freedoms.
Shaping the Future of Privacy
The legal system’s challenge is to strike a balance between individual privacy and collective well-being. This requires nuanced approaches, such as implementing transparent data usage policies, limiting the scope of surveillance, and providing judicial oversight to ensure accountability.
E-Commerce and Consumer Protection
The explosion of e-commerce has revolutionized how people shop and transact, but it has also introduced a range of legal challenges. Fraud, counterfeit products, and data theft are prevalent risks in the online marketplace, and addressing these requires innovative legal strategies.
Building Consumer Confidence
For e-commerce platforms to thrive, consumers need confidence that their rights are protected. Laws governing digital transactions include safeguards against misleading advertising, unfair pricing practices, and breaches of consumer data. Notably, these laws aim to ensure that virtual marketplaces are held to the same standards as traditional brick-and-mortar stores.
Cross-Border Trade Complexities
One significant challenge in e-commerce law is navigating cross-border transactions. With buyers and sellers often operating in different jurisdictions, disputes can arise over which country’s laws apply. The development of international agreements and arbitration mechanisms is essential to resolve such issues efficiently.
Ethical Challenges in Law Craft
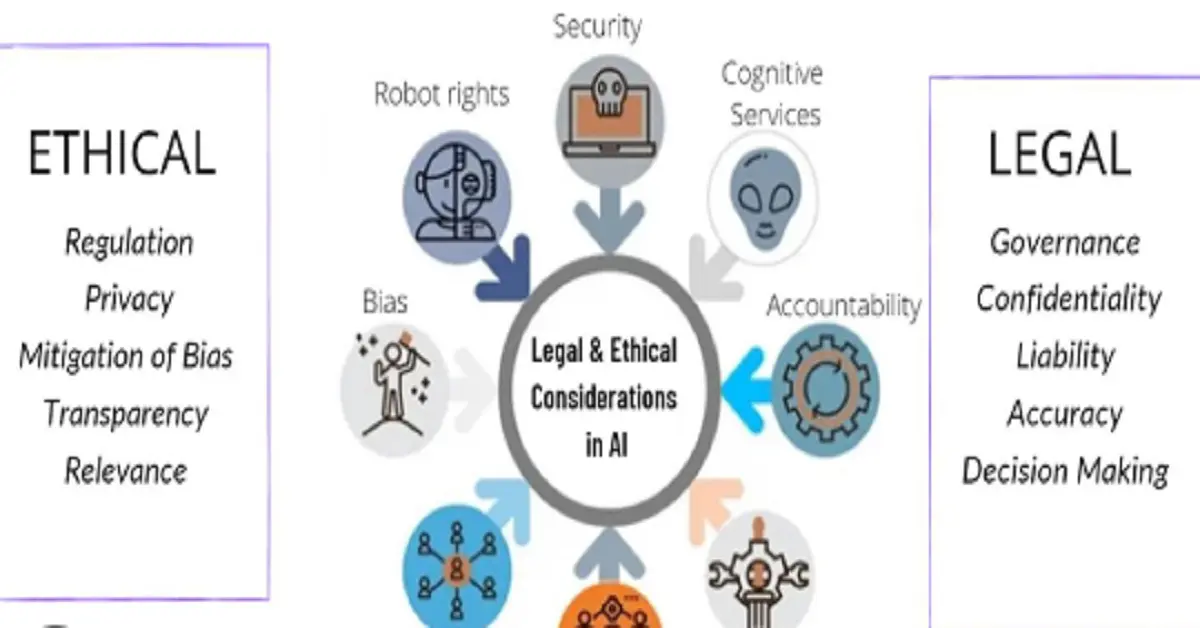
The beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age has introduced ethical dilemmas that test the very foundations of law. Legal professionals must navigate issues like algorithmic bias, transparency in AI decision-making, and the equitable application of digital regulations.
Addressing Bias in Technology
Bias in technology, especially AI, has garnered widespread attention. Algorithms used in predictive policing, loan approvals, or hiring processes can inadvertently reinforce existing inequalities. Legal systems must ensure that these tools are subject to rigorous scrutiny and align with principles of fairness and justice.
Transparency in Legal AI
Another ethical challenge lies in the use of AI in legal decision-making. While AI tools can analyze large volumes of data to predict outcomes or suggest strategies, their opacity often makes it difficult to understand how decisions are reached. Legal frameworks must mandate transparency, allowing stakeholders to review and challenge AI-driven conclusions.
Case Studies: Law Craft in Action
Examining real-world examples provides valuable insights into the successes and challenges of law in the digital age.
GDPR: A Milestone in Data Privacy
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is often cited as a benchmark for data privacy laws worldwide. It has empowered individuals by granting them greater control over their data and holding organizations accountable for its misuse. However, the law’s stringent requirements have also posed compliance challenges for businesses, particularly smaller enterprises.
Facial Recognition Technology
The adoption of facial recognition technology by law enforcement agencies has sparked debates about its effectiveness and potential for abuse. While successful in solving high-profile crimes, the technology has also faced criticism for its inaccuracies and disproportionate impact on marginalized communities. Legal systems are now grappling with setting clear boundaries for its use.
The Path Forward
The intersection of technology and law is both exciting and complex. As the beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information agecontinues to evolve, legal systems must remain agile and forward-thinking. Collaboration between technologists, lawmakers, and civil society is critical to ensure that innovation serves humanity without compromising justice, equity, or privacy.
By addressing emerging challenges with clarity and foresight, the field of law can continue to uphold its fundamental purpose: safeguarding rights, resolving disputes, and maintaining order in an increasingly digital world. The journey beyond bytes and bits is far from over, but it holds the promise of a future where law and technology coexist harmoniously for the greater good.
The Role of International Cooperation
In an interconnected world, the challenges posed by the beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age often extend beyond national borders. Issues like cybercrime, data breaches, and intellectual property theft frequently involve multiple jurisdictions, requiring international collaboration to address them effectively.
Cross-Border Legal Challenges
One of the most significant challenges in international law is managing cross-border data flows. For example, a company based in one country may store its data in another while serving customers worldwide. In such scenarios, which country’s laws apply? Resolving these jurisdictional conflicts requires harmonized frameworks that account for the complexities of the digital economy.
Similarly, cybercrime often involves actors from multiple countries. Without a unified approach to investigating, prosecuting, and extraditing offenders, many cybercriminals operate with impunity. International treaties like the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime provide a foundation for cooperation but need broader participation and modernization to remain effective.
Harmonizing Global Standards
The lack of consistency in laws across countries poses another hurdle. While some nations implement stringent data protection laws, others lag behind, creating loopholes that bad actors exploit. International organizations, such as the United Nations and the World Trade Organization, play a crucial role in fostering agreements that promote uniform standards for data privacy, cybersecurity, and intellectual property.
Emerging Trends in Legal Innovation

The beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age is not just about addressing challenges—it’s also about leveraging opportunities. Innovation is reshaping legal systems, making them more efficient, accessible, and responsive.
Blockchain in Legal Systems
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize how legal systems operate. By providing secure, tamper-proof records, blockchain can streamline processes like contract management, property registration, and dispute resolution. Smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—are already being used to automate transactions and reduce reliance on intermediaries.
Virtual Courtrooms
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of virtual courtrooms, demonstrating the feasibility of conducting legal proceedings online. While virtual hearings improve accessibility and reduce costs, they also require robust digital infrastructure and security measures to prevent disruptions or breaches.
Online Dispute Resolution (ODR)
ODR platforms are gaining traction as an efficient alternative to traditional court cases. By using technology to mediate and resolve disputes, these platforms offer faster and more cost-effective solutions for issues ranging from small claims to international trade disputes.
Preparing for the Future
As technology continues to advance, legal systems must prioritize adaptability. Preparing for the future involves not only revising outdated laws but also equipping legal professionals with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in a digital-first world.
Reforming Legal Education
Legal education is transforming to meet the demands of the beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age. Law schools are incorporating courses on cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and data privacy into their curricula. By fostering interdisciplinary learning, these programs prepare students to navigate the complex intersection of law and technology.
Encouraging Multidisciplinary Collaboration
The future of law depends on collaboration between legal experts, technologists, ethicists, and policymakers. Multidisciplinary teams can develop innovative solutions to complex problems, ensuring that laws are both technologically informed and socially equitable.
Conclusion: Shaping Justice in the Digital Era
The beyond bytes and bits: law craft in the information age has ushered in an unprecedented change and complexity for legal systems worldwide. From safeguarding privacy and combating cybercrime to fostering innovation and ensuring fairness, the challenges are as diverse as they are significant.
However, these challenges also present opportunities to rethink and improve the way the law operates. By embracing technology, fostering international collaboration, and prioritizing ethical considerations, the legal profession can keep pace with the digital revolution and shape a future where justice and innovation coexist harmoniously.
